Syncing Data to AWS S3
Business & Enterprise only
Note that syncing data to S3 is limited to the Business and Enterprise product plans. See our pricing page for more information.
Overview
Admins can configure Twingate to send audit logs, network events, and DNS filtering logs to their AWS S3 buckets in JSON format every 5 minutes. This data can be programmatically consumed or sent to a SIEM, providing real-time visibility for troubleshooting or investigating Admin actions within Twingate or end user connections across the network.
Payload Examples
Depending on selected event streams, the following event types will be pushed as separate objects in a single JSON file (filename format: 2025-07-25T18:20:00+00:00.json) about every 5 minutes.
network_access
For ZTNA tunneling events - refer to Network Events Schema for more info.
{ "event_type": "network_access", "event": { "version": 1, "time": "2025-07-25T18:19:41.236597+00:00", "status": "closed_connection", "connection": { "id": "8ffefb3db7bd8446-20", "client_ip": "1.2.3.4", "protocol": "tcp", "bytes_received": 338, "bytes_transferred": 404 }, "connector": { "id": "123456", "name": "faithful-pigeon" }, "remote_network": { "id": "789012", "name": "aws-us-east-1-dev" }, "resource": { "address": "argocd.eks.twindemo.int", "applied_rule": "argocd.eks.twindemo.int", "id": "1234567", "ip": "10.11.12.13", "port": 80 }, "relays": [ { "ip": "1.2.3.4", "name": "relaybalancer+https://relays-prm.twingate.com", "port": 30501 } ], "device": { "id": "1234567" }, "user": { "id": "890123", "email": "janedoe@twindemo.com" }, "location": { "lat": 39.84, "lon": -100.04 } }}dns_filtering
For DNS filtering events - refer to DNS Filtering Logs Schema for more info.
{ "event_type": "dns_filtering", "event": { "version": 1, "time": "2025-07-25T18:23:37.774557+00:00", "domain": "global.help-panel.docs.aws.a2z.com", "root": "a2z.com", "device": { "id": "RGV2aABCDEFGHIJKL=", "name": "Jane's MacBook Pro", "model": { "hostname": "jd-mbpro.local", "local_name": "MacBook Pro (16-inch, M1 Pro, Late 2021)", "serial_number": "XYZABC1" } }, "connection": { "client_ip": "12.34.56.78", "protocol": "DNS-over-HTTPS" }, "status": "default", "reasons": [] }}audit_log
For admin actions - refer to Audit Logs Schema for more info.
{ "event_type": "audit_log", "event": { "version": 1, "time": "2025-07-25T18:24:05.979179+00:00", "action": "create", "targets": [ { "version": "1.0", "type": "PublicAPIKey", "name": "TerraformKey", "id": "UHViABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP", "permission": "read only", "allowedIpRanges": ["0.0.0.0/0", "::/0"] } ], "actor": { "type": "User", "id": "VXNlabcdefghi=", "info": { "email": "janedoe@twindemo.com", "name": "Jane Doe" } } }}data_loss_prevention
For app control policies.
{ "event_type": "data_loss_prevention", "event": { "version": 1, "time": "2025-07-26T00:43:25.104518+00:00", "action": "block_upload", "status": "blocked", "data_loss_prevention_policies": [ { "id": "RGF0YUxabcd123efghijklmn456", "name": "DLP-AllActions-AllContent" } ], "device": { "id": "1234567", "name": "jd-mbpro" }, "user": { "id": "8901234", "email": "janedoe@twindemo.com" }, "resource": { "address": "chatgpt.com", "applied_rule": "*chatgpt.com", "id": "123456" } }}Authentication Options
Twingate offers two ways to authenticate for syncing data to AWS S3:
Option 1: OIDC IAM Role (Recommended for Most Teams)
We recommend this approach for all production environments, especially at scale.
This is the recommended approach for securely syncing data to S3. It uses short-lived, automatically rotated credentials via an IAM role that Twingate assumes through OpenID Connect (OIDC). This setup reduces risk, simplifies credential management, and aligns with AWS security best practices.
- Secure by design: no long-lived access keys
- Fine-grained access via scoped IAM roles
- Best suited for organizations with centralized identity management or those operating at scale
- Requires setting up a trusted OIDC identity provider in AWS
✅ We strongly recommend this method for all production environments.
Option 2: IAM User Credentials (Supported for Simpler Setups)
For smaller teams or simpler environments without an identity provider, you can also configure S3 sync using static IAM user credentials. While still supported, this method requires careful handling due to its reliance on long-lived access keys and manual rotation.
- Relies on static credentials that must be rotated manually
- Lower overhead, but less secure than OIDC
- Best suited for smaller teams or environments without an identity provider
- Not recommended for production or regulated environments
⚠️ If you use this method, ensure your access keys are tightly controlled and monitored. Consider transitioning to the OIDC method when possible.
Setup Methods
You can configure either authentication option using:
- Web UI — via the Twingate Admin Console (see below)
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) — via Terraform. See example below.
Step 1: Create or Identify Your AWS S3 Bucket
Follow the AWS S3 User Guide to create a bucket. Twingate will write logs to this bucket in JSON format.
Step 2: Configure AWS Permissions
Required IAM Policy
Ensure the IAM Role includes an inline or attached policy that grants s3:PutObject on your S3 bucket. If you’re using SSE-KMS encryption, you’ll also need permissions for kms:GenerateDataKey* and kms:Decrypt.
S3 Sync Permissions
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "TwingateS3Sync", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "s3:PutObject", "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<S3BucketName>/*" } ]}S3 Sync Permissions with SSE-KMS Encryption
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "TwingateS3Sync", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": ["s3:PutObject", "kms:GenerateDataKey*", "kms:Decrypt"], "Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<S3BucketName>/*" } ]}Option 1: OIDC IAM Role (Recommended)
-
Create an IAM Identity Provider
- Log into AWS
- Navigate to IAM → Identity Providers → Add provider
- Choose OpenID Connect
- Provider URL:
https://<your-network>.twingate.com/oidcFor the provider URL, enter your Network’s URL followed byoidc. For example, if your Network’s URL ishttps://acme.twingate.com, your provider URL should behttps://acme.twingate.com/oidc - Audience:
<your-network-slug>For the audience field, use your Network’s slug (e.g.,acme, fromacme.twingate.com)
-
Create a Policy
- Navigate to IAM → Policies → Create policy
- Grant your IAM Identity Provider User access to the bucket. Make sure the user has
s3:PutObjectlisted in their policy (see above callout). - If your S3 bucket uses an encryption method other than the default SSE-S3 encryption, additional permissions are necessary. For example, if using SSE-KMS encryption, add another statement granting
kms:GenerateDataKey*andkms:Decrypt(see example above).
-
Create the IAM Role
-
Navigate to IAM → Roles → Create role
-
Trusted entity: Web identity
-
Provider: the OIDC provider you created in the previous step
-
Audience: your network slug (e.g.,
acme) -
Add condition:
- Key:
<your-network>.twingate.com/oidc:sub - Operator:
StringEquals - Value:
events_sync
- Key:
-
Attach the IAM policy you created in the previous step
-
Name your role (e.g.,
TwingateS3SyncRole) -
Create the role
-
Option 2: IAM User Credentials
-
Create an IAM User
-
Create a static IAM user that will be used by the Twingate S3 Sync to access the S3 bucket.
-
Navigate to IAM → Users → Create user
-
-
Create and Assign Policy
-
Create IAM policy allowing
S3:PutObjectfor IAM User. -
Grant your AWS S3 user access to the bucket. Make sure the user has
s3:PutObjectlisted in their policy (see above callout).
-
-
Provision Access Keys
- Generate and securely store the Access Key and Secret Access Key
- Select the user who should have access to the S3 bucket
- Click Create access key
- Save the Access Key and Secret Access Key (will need these later)
-
Ensure Correct Permissions on S3 Bucket
- Create or update IAM policy allowing
S3:PutObjecton S3 bucket, and (optionally) restrict access to IAM User.
{"Version": "2012-10-17","Statement": [{"Sid": "AllowTwingateUserToPutObject","Effect": "Allow","Principal": { "AWS": "aws_iam_user.twingate_s3_user.arn" },"Action": ["s3:PutObject"],"Resource": "${local.bucket_arn}/*"}]} - Create or update IAM policy allowing
Step 3: Configure your AWS S3 sync in the Twingate Admin Console
- Go to Settings → Reports
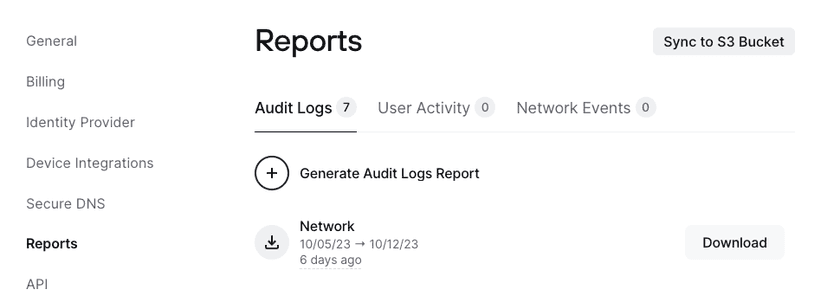
- Click Sync to S3 Bucket
- Choose your authentication method:
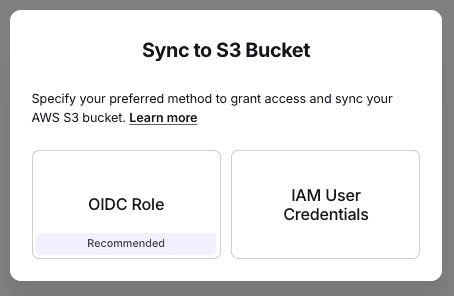
Option Required Info OIDC Role Bucket name & IAM Role ARN IAM Credentials Bucket name, Access Key & Secret
💡 Do not include the
arn:aws:s3:::prefix when entering the bucket name.
- Logs should start syncing within 10 minutes. Any subsequent audit log, network events, and DNS filtering logs will be synced to your S3 bucket every 5 minutes on an ongoing basis.
(Optional) Configure Using Terraform
If you’re managing infrastructure with Terraform, below are example configurations or you can take a look at our Terraform Examples.
Terraform Compatibility
These examples were last tested with:
- Terraform:
v1.12.2 - AWS Provider:
~> 6.0.0
Be sure to validate these versions with your environment or pin them using the required_providers block in your Terraform configuration.
OIDC Example
terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "~> 6.0.0" } } required_version = ">= 1.12.2"}
# The Twingate network slug, used for OIDC URL and audiencevariable "tenant_slug" { type = string description = "Twingate network slug (e.g., acme)" default = "<tenant>"}
# Name of the S3 bucket to receive logsvariable "bucket_name" { type = string description = "S3 bucket name for Twingate sync" default = "<bucket-name>"}
# Defining reusable valueslocals { oidc_url = "https://${var.tenant_slug}.twingate.com/oidc" oidc_prefix = "${var.tenant_slug}.twingate.com/oidc" bucket_arn = "arn:aws:s3:::${var.bucket_name}"}
# OIDC provider: allows AWS to validate tokens issued by Twingateresource "aws_iam_openid_connect_provider" "twingate" { url = local.oidc_url client_id_list = [var.tenant_slug]}
# IAM policy assigned to the role: grants Twingate permission to upload logsresource "aws_iam_policy" "twingate_s3_sync" { name = "${var.tenant_slug}-twingate-s3-sync-2" description = "Allows Twingate to upload logs to S3"
policy = jsonencode({ Version = "2012-10-17" Statement = [ { Sid = "TwingateS3Sync" Effect = "Allow" Action = "s3:PutObject" Resource = [ "${local.bucket_arn}/*" ] } ] })}
# IAM role assumed by Twingate via OIDC for secure log syncresource "aws_iam_role" "twingate_s3_sync" { name = "${var.tenant_slug}-twingate-s3-sync-role"
assume_role_policy = jsonencode({ Version = "2012-10-17" Statement = [{ Effect = "Allow" Principal = { Federated = aws_iam_openid_connect_provider.twingate.arn } Action = "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity" Condition = { StringEquals = { "${local.oidc_prefix}:aud" = var.tenant_slug "${local.oidc_prefix}:sub" = "events_sync" } } }] })}
# Attach above policy to the IAM roleresource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "twingate_attach" { role = aws_iam_role.twingate_s3_sync.name policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.twingate_s3_sync.arn}
# Create or manage the S3 bucket for log storageresource "aws_s3_bucket" "logs" { bucket = var.bucket_name}
# Bucket policy: grants only the sync role permission to put objectsresource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "logs" { bucket = aws_s3_bucket.logs.id
policy = jsonencode({ Version = "2012-10-17" Statement = [{ Sid = "TwingateS3Sync" Effect = "Allow" Principal = { AWS = aws_iam_role.twingate_s3_sync.arn } Action = ["s3:PutObject"] Resource = [ "${local.bucket_arn}/*" ] }] })}
# Output to grab the aws_iam_role arn => to be used in Twingateoutput "twingate_s3_sync_role_arn" { description = "IAM Role ARN that Twingate uses to upload logs" value = aws_iam_role.twingate_s3_sync.arn}IAM User Example
terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "~> 6.0.0" } } required_version = ">= 1.12.2"}
# The Twingate network slug (used for tagging and naming)variable "tenant_slug" { type = string description = "Twingate network slug (e.g., acme)" default = "twindemogb"}
# Name of the S3 bucket to receive logsvariable "bucket_name" { type = string description = "S3 bucket name for Twingate sync" default = "test-twindemogb-logs"}
# Defining reusable valueslocals { bucket_arn = "arn:aws:s3:::${var.bucket_name}"}
# IAM user for static accessresource "aws_iam_user" "twingate_s3_user" { name = "${var.tenant_slug}-s3-sync-user"}
# IAM policy allowing S3 PutObjectresource "aws_iam_policy" "twingate_s3_policy" { name = "${var.tenant_slug}-s3-sync-policy" description = "Allows PutObject to Twingate log bucket"
policy = jsonencode({ Version = "2012-10-17" Statement = [ { Effect = "Allow" Action = ["s3:PutObject"] Resource = [ local.bucket_arn, "${local.bucket_arn}/*" ] } ] })}
# Attach the policy to the userresource "aws_iam_user_policy_attachment" "twingate_user_attach" { user = aws_iam_user.twingate_s3_user.name policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.twingate_s3_policy.arn}
# Create access keys for the userresource "aws_iam_access_key" "twingate_s3_access_key" { user = aws_iam_user.twingate_s3_user.name}
# Create or manage the S3 bucketresource "aws_s3_bucket" "logs" { bucket = var.bucket_name}
# Optional: S3 bucket policy (if you want to restrict writes to this IAM user specifically)resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "logs" { bucket = aws_s3_bucket.logs.id
policy = jsonencode({ Version = "2012-10-17" Statement = [ { Sid = "AllowTwingateUserToPutObject", Effect = "Allow", Principal = { AWS = aws_iam_user.twingate_s3_user.arn }, Action = ["s3:PutObject"], Resource = "${local.bucket_arn}/*" } ] })}
# Outputs for Twingate Admin Consoleoutput "access_key_id" { value = aws_iam_access_key.twingate_s3_access_key.id description = "Access Key ID for Twingate S3 sync"}
output "secret_access_key" { value = aws_iam_access_key.twingate_s3_access_key.secret description = "Secret Access Key for Twingate S3 sync" sensitive = true}
output "bucket_name" { value = var.bucket_name description = "S3 bucket name (no ARN prefix)"}Troubleshooting
Why is my S3 sync failing?
If you’ve just configured your S3 sync and it immediately fails, you could be running into a configuration issue. Please check that your bucket name, access key, secret access key, and AWS user policies are correct. The AWS user must have a policy granting s3:PutObject access to the target bucket.
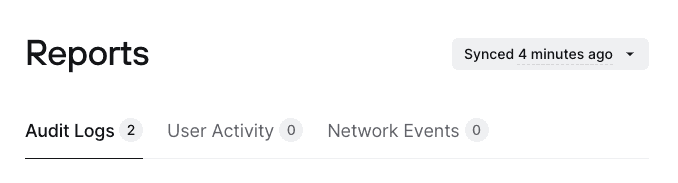
What happens if there are no events to sync?
In the case that there are no events to sync, Twingate will not send files to the S3 bucket. You can confirm that the sync works in the Admin Console by navigating to Settings, then Reports. The S3 sync status will be displayed on the upper right corner as seen below.
I just performed an action that should be reflected in my data. Why am I not seeing it?
Events can take up to 10 minutes to be reflected in the sync.
What permissions does my AWS Admin user need to do these actions (Console, API, Terraform)?
Admin IAM User Permissions
These are the necessary permissions that the AWS IAM Admin User needs to create the OIDC or static IAM user:
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "AdditionalAllow", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "iam:CreateRole", "iam:AttachRolePolicy", "iam:DeleteRole", "iam:DetachRolePolicy", "iam:PassRole", "iam:CreateOpenIDConnectProvider", "iam:DeleteOpenIDConnectProvider", "iam:CreatePolicy", "iam:DeletePolicy", "iam:CreatePolicyVersion", "iam:DeletePolicyVersion", "S3:PutObject", "iam:CreateUser", "iam:DeleteUser", "iam:UpdateUser", "iam:AttachUserPolicy", "iam:DetachUserPolicy", "iam:CreateAccessKey", "iam:DeleteAccessKey", "iam:UpdateAccessKey", "iam:ListAccessKeys" ], "Resource": ["*"] } ]}Last updated 5 months ago