How to Deploy a Connector on GCP
Overview
There are several options available for deploying Connectors on Google Cloud Platform depending on your particular environment and needs.
Check your subnet configuration
The subnet you deploy a Connector in requires outbound Internet access, both to download the Connector container image and to connect to Twingate. Check our Best Practices for Connectors guide for more information.
Peer-to-peer connections help you to provide a better experience for your users and to stay within the Fair Use Policy for bandwidth consumption. Learn how to support peer-to-peer connections.
Compute Engine Deployment
If you are deploying a custom virtual machine, you can follow the general Linux Connector deployment instructions for full details.
In summary:
- Docker-based deployment is compatible with any 64-bit Linux distribution that Docker supports.
- The Connector
systemdservice is currently supported on Ubuntu, Fedora, Debian, and CentOS.
Please see our Connector Best Practices overview for general recommendations as well as hardware recommendations for Google Cloud.
Automated Compute Engine Deployment
We offer an automated method of deploying a Compute Engine instance with the Connector pre-installed. Use the steps below to create and configure a Compute Engine instance.
- Log in to your Twingate Admin Console, click on Remote Networks then on the Remote Network on which you want to deploy a Connector. From there, scroll down and click on the Add Connector button on the left-hand side of the screen
- Click on the new Connector that was created. On the deployment page click the Google Cloud option at the top of the screen
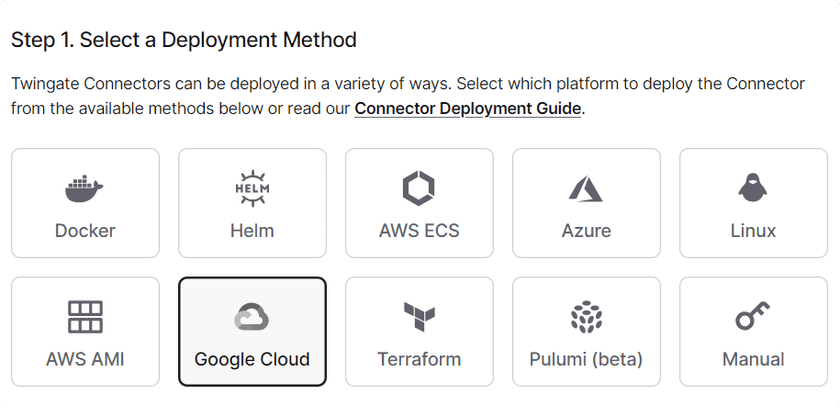
Choosing the ECS Option - Scroll down to step 2 and click the button to generate tokens. It will have you re-authenticate and then bring you back to this page
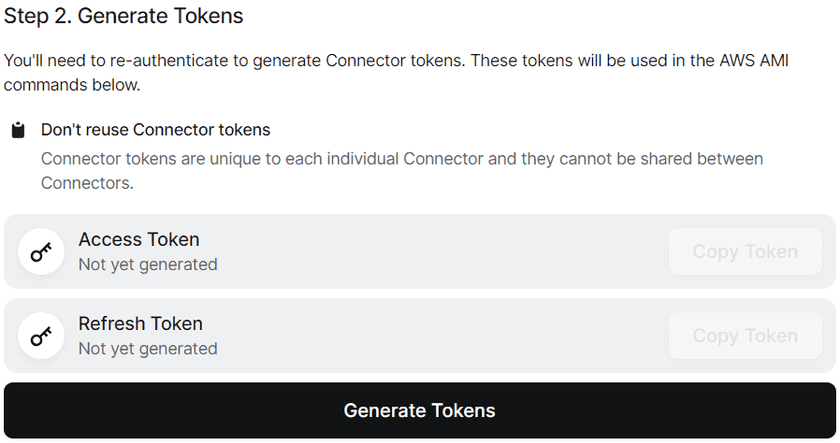
Generate Tokens - Scroll down to step 3 and fill out the required information about your Google Cloud environment, as well as enable and configure the optional features
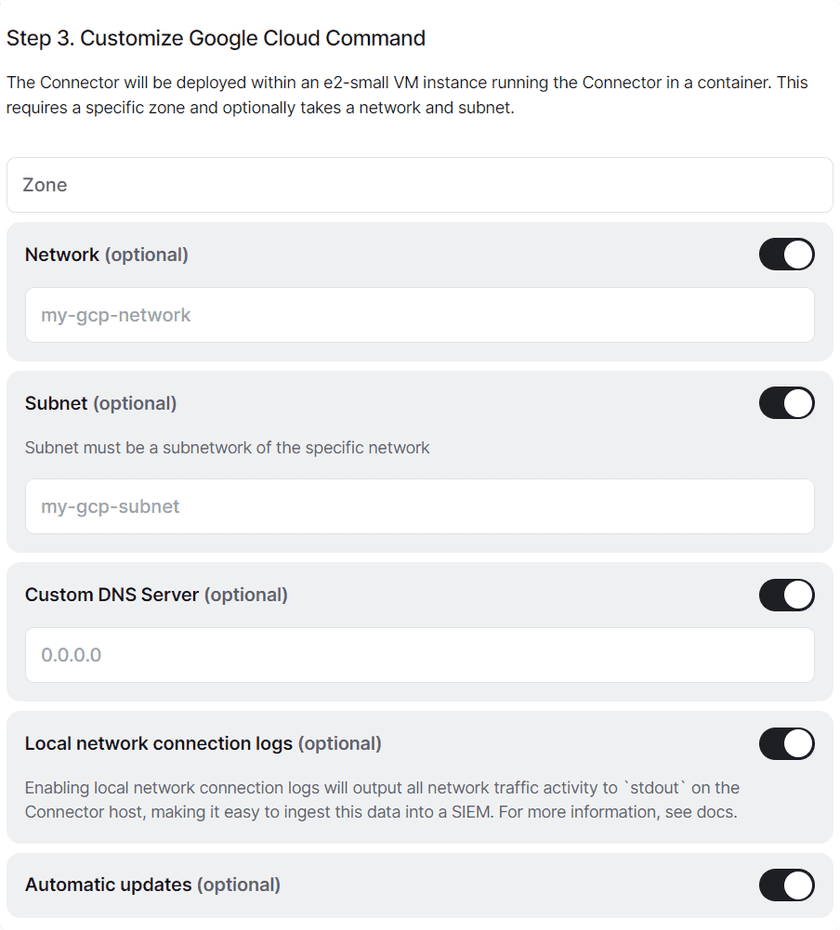
Fill out the ECS Configuration - Scroll down to step 5 and copy the command to launch the Connector. Run it in the Google Cloud CLI
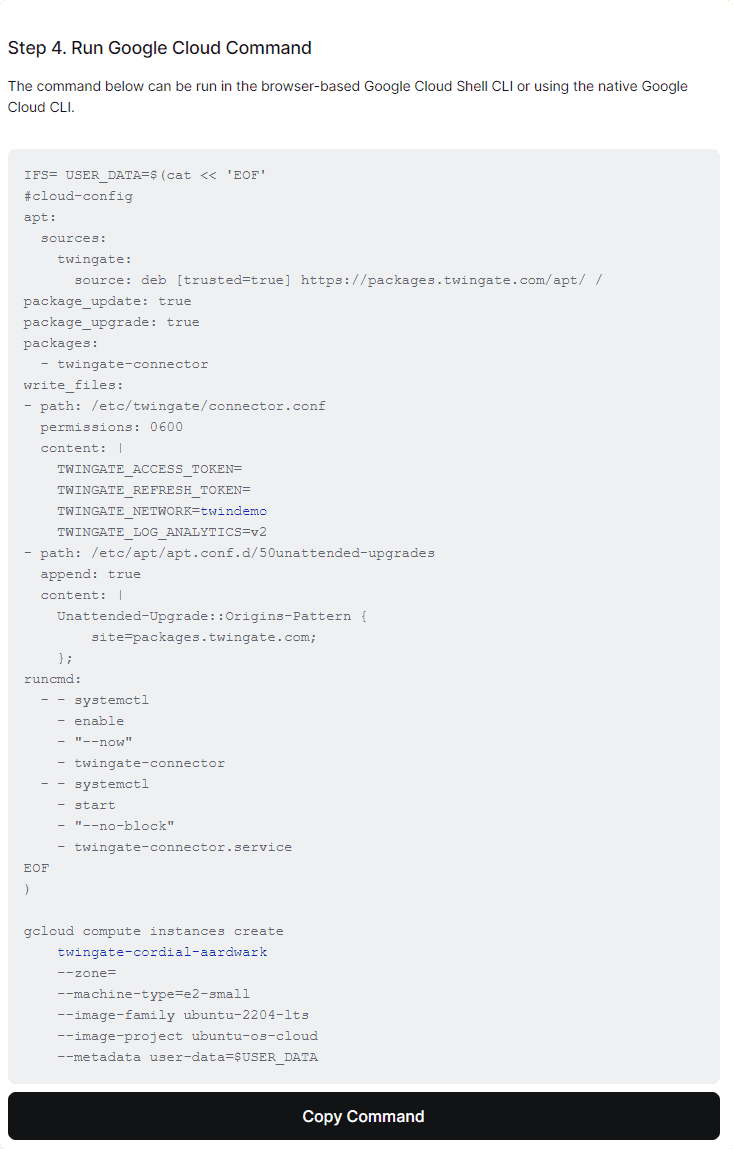
Launch the Connector
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Deployment
Connectors can also be deployed on a GKE cluster using the official Twingate Helm chart. If you intend use Twingate for K8s, you may also want to look at our Kubernetes Best Practices Guide.
Infrastructure as Code Deployment
Deployment automation is available using Terraform, Pulumi, or the Twingate API.
Access and refresh tokens, which are required for Connector deployment, are specific to an individual Connector and cannot be shared between multiple Connectors.
Updating the Connector
Connectors running on GCP run as a systemd service. Updates can be done manually by using the Linux package manager, or automatically by setting up a scheduled task to check for updates. We recommend staggering updates across multiple Connectors to avoid downtime. For more details check our Systemd Connector Update Guide.
Last updated 3 months ago